Merge branch 'master' of https://gitee.com/huangge1199_admin/leet-code
This commit is contained in:
commit
e68766204e
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
||||
//给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值
|
||||
//都不同。
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 示例 1:
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
|
||||
//输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
|
||||
//解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 示例 2:
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//输入:root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25
|
||||
//输出:[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 示例 3:
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5
|
||||
//输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 提示:
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 给定的树上的节点数介于 0 和 10^4 之间
|
||||
// 每个节点都有一个唯一整数值,取值范围从 0 到 10^8
|
||||
// -10^8 <= val <= 10^8
|
||||
// 新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Related Topics 树 二叉搜索树 二叉树 👍 229 👎 0
|
||||
|
||||
package leetcode.editor.cn;
|
||||
|
||||
import com.code.leet.entiy.TreeNode;
|
||||
|
||||
//701:二叉搜索树中的插入操作
|
||||
class InsertIntoABinarySearchTree {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
//测试代码
|
||||
Solution solution = new InsertIntoABinarySearchTree().new Solution();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//力扣代码
|
||||
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* public class TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode left;
|
||||
* TreeNode right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
|
||||
* this.val = val;
|
||||
* this.left = left;
|
||||
* this.right = right;
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
|
||||
if (root == null) {
|
||||
return new TreeNode(val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
TreeNode node = root;
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
if (node.val > val) {
|
||||
if (node.left == null) {
|
||||
node.left = new TreeNode(val);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
node = node.left;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (node.right == null) {
|
||||
node.right = new TreeNode(val);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
node = node.right;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
//给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 示例:
|
||||
//给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 3
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 9 20
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 15 7
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 返回它的最大深度 3 。
|
||||
// Related Topics 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 二叉树 👍 1012 👎 0
|
||||
|
||||
package leetcode.editor.cn;
|
||||
|
||||
import com.code.leet.entiy.TreeNode;
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.LinkedList;
|
||||
import java.util.Queue;
|
||||
|
||||
//104:二叉树的最大深度
|
||||
class MaximumDepthOfBinaryTree {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
//测试代码
|
||||
Solution solution = new MaximumDepthOfBinaryTree().new Solution();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//力扣代码
|
||||
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* public class TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode left;
|
||||
* TreeNode right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
|
||||
* this.val = val;
|
||||
* this.left = left;
|
||||
* this.right = right;
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
if (root == null) {
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
|
||||
queue.add(root);
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
|
||||
int size = queue.size();
|
||||
if (size > 0) {
|
||||
count++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
||||
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
|
||||
assert node != null;
|
||||
if (node.left != null) {
|
||||
queue.add(node.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node.right != null) {
|
||||
queue.add(node.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
//给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个值。 你需要在BST中找到节点值等于给定值的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 NULL。
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 例如,
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//给定二叉搜索树:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 4
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 2 7
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 1 3
|
||||
//
|
||||
//和值: 2
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 你应该返回如下子树:
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 2
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 1 3
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 在上述示例中,如果要找的值是 5,但因为没有节点值为 5,我们应该返回 NULL。
|
||||
// Related Topics 树 二叉搜索树 二叉树 👍 162 👎 0
|
||||
|
||||
package leetcode.editor.cn;
|
||||
|
||||
import com.code.leet.entiy.TreeNode;
|
||||
|
||||
//700:二叉搜索树中的搜索
|
||||
class SearchInABinarySearchTree {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
//测试代码
|
||||
Solution solution = new SearchInABinarySearchTree().new Solution();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//力扣代码
|
||||
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* public class TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode left;
|
||||
* TreeNode right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
|
||||
* this.val = val;
|
||||
* this.left = left;
|
||||
* this.right = right;
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
|
||||
while (root != null && root.val != val) {
|
||||
if (root.val > val) {
|
||||
root = root.left;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
root = root.right;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return root;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
84
src/main/java/leetcode/editor/cn/SymmetricTree.java
Normal file
84
src/main/java/leetcode/editor/cn/SymmetricTree.java
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
//给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 2 2
|
||||
// / \ / \
|
||||
//3 4 4 3
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1
|
||||
// / \
|
||||
// 2 2
|
||||
// \ \
|
||||
// 3 3
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 进阶:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
|
||||
// Related Topics 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 二叉树 👍 1583 👎 0
|
||||
|
||||
package leetcode.editor.cn;
|
||||
|
||||
import com.code.leet.entiy.TreeNode;
|
||||
|
||||
//101:对称二叉树
|
||||
class SymmetricTree {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
//测试代码
|
||||
Solution solution = new SymmetricTree().new Solution();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//力扣代码
|
||||
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Definition for a binary tree node.
|
||||
* public class TreeNode {
|
||||
* int val;
|
||||
* TreeNode left;
|
||||
* TreeNode right;
|
||||
* TreeNode() {}
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
|
||||
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
|
||||
* this.val = val;
|
||||
* this.left = left;
|
||||
* this.right = right;
|
||||
* }
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
return dfs(root.left, root.right);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private boolean dfs(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
|
||||
if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (node1.val != node2.val) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!dfs(node1.left, node2.right)) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dfs(node1.right, node2.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<p>给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 <strong>保证</strong> ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意</strong>,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 <strong>任意有效的结果</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2020/10/05/insertbst.jpg" style="width: 752px; height: 221px;" />
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[4,2,7,1,3,5]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2020/10/05/bst.jpg" style="width: 352px; height: 301px;" />
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[4,2,7,1,3,5]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>给定的树上的节点数介于 <code>0</code> 和 <code>10^4</code> 之间</li>
|
||||
<li>每个节点都有一个唯一整数值,取值范围从 <code>0</code> 到 <code>10^8</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10^8 <= val <= 10^8</code></li>
|
||||
<li>新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
<div><div>Related Topics</div><div><li>树</li><li>二叉搜索树</li><li>二叉树</li></div></div><br><div><li>👍 229</li><li>👎 0</li></div>
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>说明:</strong> 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong><br>
|
||||
给定二叉树 <code>[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]</code>,</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 3
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
9 20
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
15 7</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回它的最大深度 3 。</p>
|
||||
<div><div>Related Topics</div><div><li>树</li><li>深度优先搜索</li><li>广度优先搜索</li><li>二叉树</li></div></div><br><div><li>👍 1012</li><li>👎 0</li></div>
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
<p>给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个值。 你需要在BST中找到节点值等于给定值的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 NULL。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如,</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
给定二叉搜索树:
|
||||
|
||||
4
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
2 7
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
1 3
|
||||
|
||||
和值: 2
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你应该返回如下子树:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
2
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
1 3
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在上述示例中,如果要找的值是 <code>5</code>,但因为没有节点值为 <code>5</code>,我们应该返回 <code>NULL</code>。</p>
|
||||
<div><div>Related Topics</div><div><li>树</li><li>二叉搜索树</li><li>二叉树</li></div></div><br><div><li>👍 162</li><li>👎 0</li></div>
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如,二叉树 <code>[1,2,2,3,4,4,3]</code> 是对称的。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 1
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
2 2
|
||||
/ \ / \
|
||||
3 4 4 3
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>但是下面这个 <code>[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]</code> 则不是镜像对称的:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 1
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
2 2
|
||||
\ \
|
||||
3 3
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>进阶:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?</p>
|
||||
<div><div>Related Topics</div><div><li>树</li><li>深度优先搜索</li><li>广度优先搜索</li><li>二叉树</li></div></div><br><div><li>👍 1583</li><li>👎 0</li></div>
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,232 @@
|
||||
### 📺 视频题解
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 📖 文字题解
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法一:递归
|
||||
|
||||
**思路和算法**
|
||||
|
||||
如果一个树的左子树与右子树镜像对称,那么这个树是对称的。
|
||||
|
||||
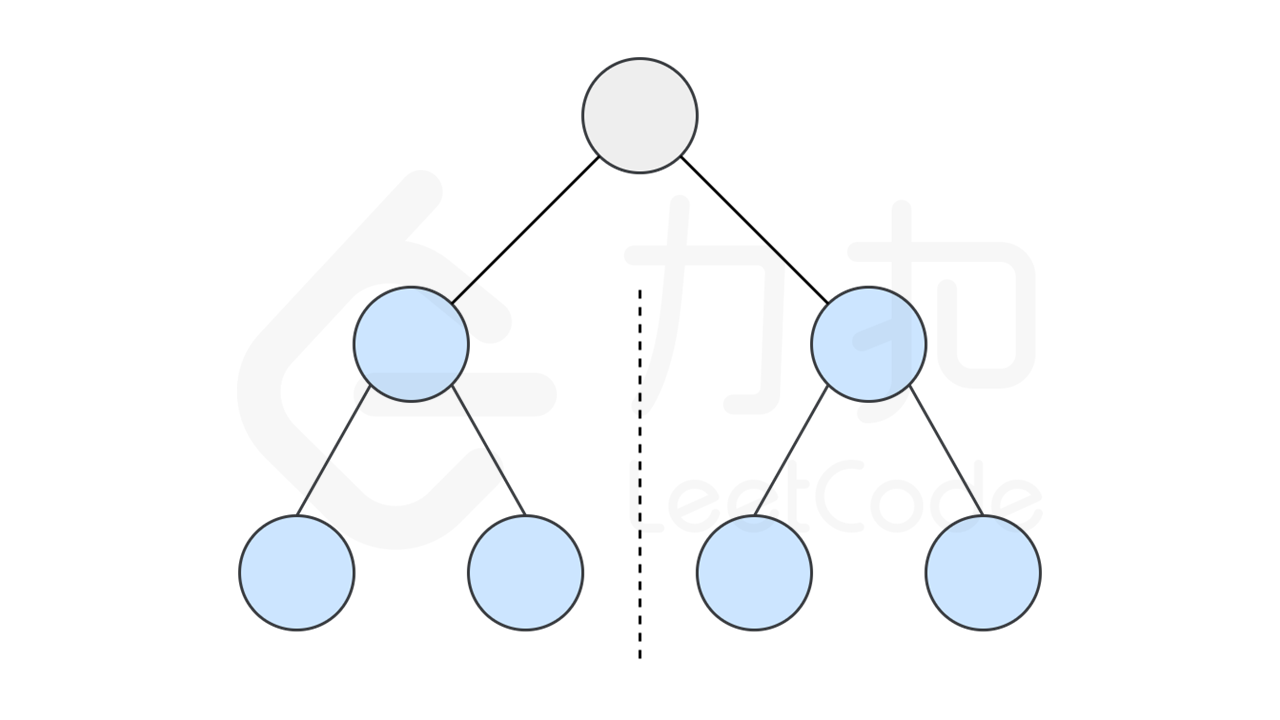
|
||||
|
||||
因此,该问题可以转化为:两个树在什么情况下互为镜像?
|
||||
|
||||
如果同时满足下面的条件,两个树互为镜像:
|
||||
|
||||
+ 它们的两个根结点具有相同的值
|
||||
+ 每个树的右子树都与另一个树的左子树镜像对称
|
||||
|
||||
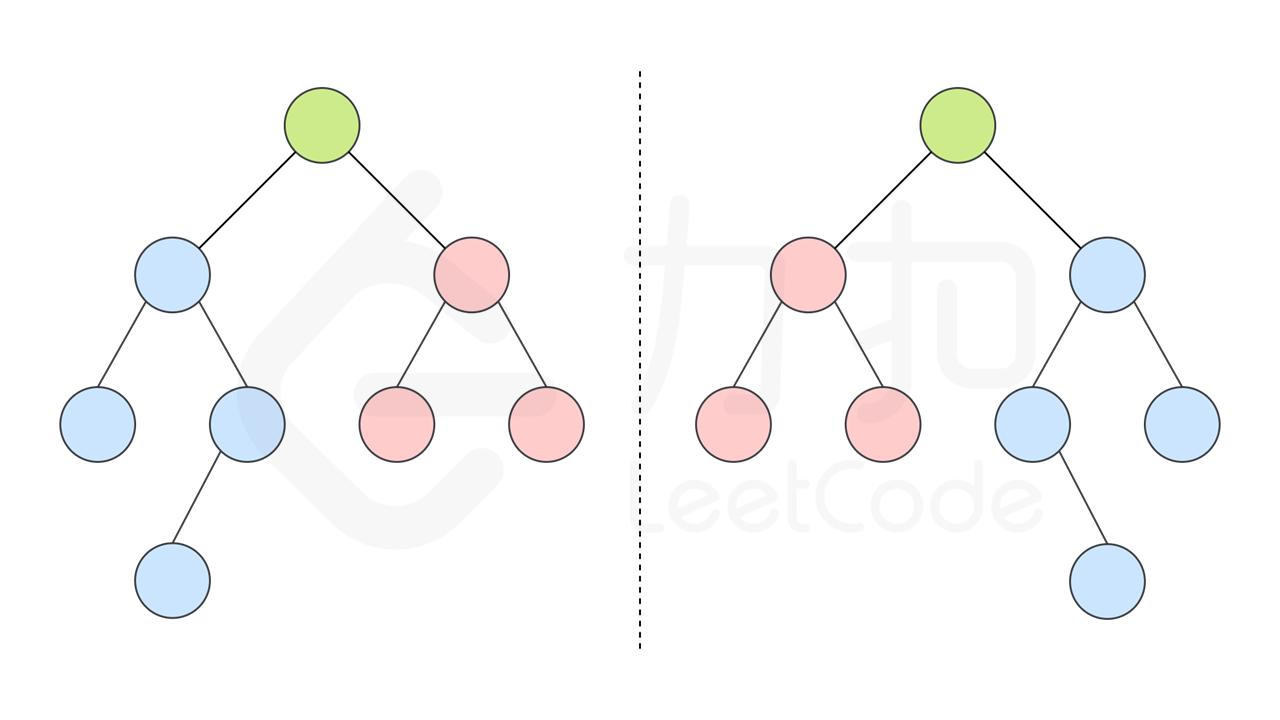
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以实现这样一个递归函数,通过「同步移动」两个指针的方法来遍历这棵树,$p$ 指针和 $q$ 指针一开始都指向这棵树的根,随后 $p$ 右移时,$q$ 左移,$p$ 左移时,$q$ 右移。每次检查当前 $p$ 和 $q$ 节点的值是否相等,如果相等再判断左右子树是否对称。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下。
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol1-C++]
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool check(TreeNode *p, TreeNode *q) {
|
||||
if (!p && !q) return true;
|
||||
if (!p || !q) return false;
|
||||
return p->val == q->val && check(p->left, q->right) && check(p->right, q->left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
|
||||
return check(root, root);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol1-Java]
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
return check(root, root);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
|
||||
if (p == null && q == null) {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (p == null || q == null) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol1-Golang]
|
||||
|
||||
```golang
|
||||
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
|
||||
return check(root, root)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func check(p, q *TreeNode) bool {
|
||||
if p == nil && q == nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p == nil || q == nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p.Val == q.Val && check(p.Left, q.Right) && check(p.Right, q.Left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol1-TypeScript]
|
||||
|
||||
```TypeScript
|
||||
const check = (p: TreeNode | null, q: TreeNode | null): boolean => {
|
||||
if (!p && !q) return true;
|
||||
if (!p || !q) return false;
|
||||
return p.val === q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
var isSymmetric = function(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
return check(root, root);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**复杂度分析**
|
||||
|
||||
假设树上一共 $n$ 个节点。
|
||||
|
||||
+ 时间复杂度:这里遍历了这棵树,渐进时间复杂度为 $O(n)$。
|
||||
+ 空间复杂度:这里的空间复杂度和递归使用的栈空间有关,这里递归层数不超过 $n$,故渐进空间复杂度为 $O(n)$。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法二:迭代
|
||||
|
||||
**思路和算法**
|
||||
|
||||
「方法一」中我们用递归的方法实现了对称性的判断,那么如何用迭代的方法实现呢?首先我们引入一个队列,这是把递归程序改写成迭代程序的常用方法。初始化时我们把根节点入队两次。每次提取两个结点并比较它们的值(队列中每两个连续的结点应该是相等的,而且它们的子树互为镜像),然后将两个结点的左右子结点按相反的顺序插入队列中。当队列为空时,或者我们检测到树不对称(即从队列中取出两个不相等的连续结点)时,该算法结束。
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol2-C++]
|
||||
|
||||
```cpp
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
bool check(TreeNode *u, TreeNode *v) {
|
||||
queue <TreeNode*> q;
|
||||
q.push(u); q.push(v);
|
||||
while (!q.empty()) {
|
||||
u = q.front(); q.pop();
|
||||
v = q.front(); q.pop();
|
||||
if (!u && !v) continue;
|
||||
if ((!u || !v) || (u->val != v->val)) return false;
|
||||
|
||||
q.push(u->left);
|
||||
q.push(v->right);
|
||||
|
||||
q.push(u->right);
|
||||
q.push(v->left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
|
||||
return check(root, root);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol2-Java]
|
||||
|
||||
```Java
|
||||
class Solution {
|
||||
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
|
||||
return check(root, root);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public boolean check(TreeNode u, TreeNode v) {
|
||||
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
|
||||
q.offer(u);
|
||||
q.offer(v);
|
||||
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
|
||||
u = q.poll();
|
||||
v = q.poll();
|
||||
if (u == null && v == null) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ((u == null || v == null) || (u.val != v.val)) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
q.offer(u.left);
|
||||
q.offer(v.right);
|
||||
|
||||
q.offer(u.right);
|
||||
q.offer(v.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol2-Golang]
|
||||
|
||||
```golang
|
||||
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
|
||||
u, v := root, root
|
||||
q := []*TreeNode{}
|
||||
q = append(q, u)
|
||||
q = append(q, v)
|
||||
for len(q) > 0 {
|
||||
u, v = q[0], q[1]
|
||||
q = q[2:]
|
||||
if u == nil && v == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if u == nil || v == nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if u.Val != v.Val {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
q = append(q, u.Left)
|
||||
q = append(q, v.Right)
|
||||
|
||||
q = append(q, u.Right)
|
||||
q = append(q, v.Left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* [sol2-TypeScript]
|
||||
|
||||
```TypeScript
|
||||
const check = (u: TreeNode | null, v: TreeNode | null): boolean => {
|
||||
const q: (TreeNode | null)[] = [];
|
||||
q.push(u),q.push(v);
|
||||
|
||||
while (q.length) {
|
||||
u = q.shift()!;
|
||||
v = q.shift()!;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!u && !v) continue;
|
||||
if ((!u || !v) || (u.val !== v.val)) return false;
|
||||
|
||||
q.push(u.left);
|
||||
q.push(v.right);
|
||||
|
||||
q.push(u.right);
|
||||
q.push(v.left);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
var isSymmetric = function(root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
|
||||
return check(root, root);
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**复杂度分析**
|
||||
|
||||
+ 时间复杂度:$O(n)$,同「方法一」。
|
||||
+ 空间复杂度:这里需要用一个队列来维护节点,每个节点最多进队一次,出队一次,队列中最多不会超过 $n$ 个点,故渐进空间复杂度为 $O(n)$。
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user